What is Lean Manufacturing
Lean Manufacturing is a term used to describe a production facility that has implemented lean tools to improve its business processes. Businesses that are running lean are always looking for ways to improve and have systems in place to track progress throughout their processes.
Many Process or Manufacturing Engineers understand the tools and steps required to help a business achieve Lean Manufacturing. In this article, we will review the benefits of implementing lean tools and some of the steps that you and your team can take to achieve a Lean Manufacturing business.
Origins of Lean Manufacturing
In the 1950s and 60s, Toyota in Japan was looking to improve their production efficiency after World War II. To achieve this, they adopted lean principles that were later adopted by many Japanese companies. Toyota implemented several lean tools that we will feature in the following section of this article. Lean manufacturing played a crucial role in building the Japanese economy and making Toyota one of the world’s leading car manufacturers.
Benefits of Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing offers several benefits to companies, but the most significant one is the potential cost savings. By identifying and reducing waste in your process, you can improve efficiency and profitability. Every time you address a bottleneck or issue in your process, you’re effectively putting more money back into your pocket.
Additionally, Lean Manufacturing can contribute to a safer work environment by promoting cleanliness and organization. When work areas are tidy and free of clutter, there is less chance of accidents or injuries occurring. In fact, statistics show that companies that implement Lean Manufacturing have fewer injuries per person than those that don’t.
Another benefit of Lean Manufacturing is that it can boost morale throughout your company. By asking for suggestions and feedback from staff on how to improve their work areas, your company will show that they value their opinions. This can help foster a more positive work environment and create a sense of ownership among workers.
How To Start Lean Manufacturing
I have been asked this question several times in the past, and my answer often varies depending on the business and the current state of Lean Manufacturing. When I investigate a process, I always start by examining what is currently implemented and what needs improvement or fixing. For this scenario, I will assume that the company has not started any Lean projects and is relatively new to the concept. To begin, I would suggest implementing the basic Lean tools.
- Kaizen – Work on small improvements
- Gemba – Fix issues in the process one walk at a time
- 5S – Organize your work areas
- Kanban – Once the parts are put away, you can start to implement your Kanban ordering system
- One Piece Flow – Adapt your process to a one-piece flow
- Line Balancing – Develop your standard operating procedures and balance your production line
Again, It really depends what your business has implemented and what you believe is a priority.
My Favorite Lean Tools
I do have my favorite Lean Tools and this is based on what I believe would be the biggest impact on a process or business. From my experience, I like these tools because they are easy to implement and you can see a very good reward when done correctly.
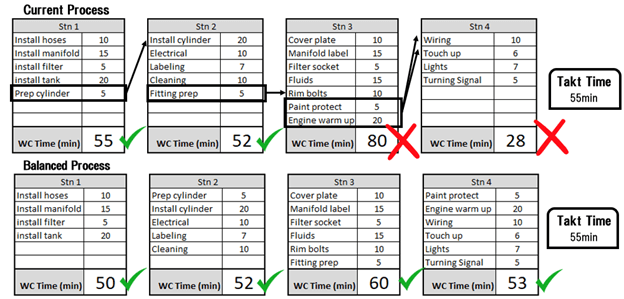
Line Balancing
I have observed that implementing a simple line balance technique can lead to significant improvements in the production process. By ensuring that each work area receives an equal amount of work time, bottlenecks can be eliminated, and the efficiency of the production line can be improved.
To illustrate this point, consider two production lines, where one is balanced and the other is not. In the unbalanced line, some staff members may have idle time while others are overworked. This can lead to bottlenecks, as staff members in certain areas may be waiting for work to be assigned to them, while other areas are busy. In contrast, a balanced line ensures that all staff members work equally, resulting in a more efficient production process.
One Piece Flow
If you are not familiar with the concept of one-piece flow, it refers to a workflow in which only one piece or part can be worked on and completed at a time. When you have a balanced line and you work on one assembly at a time, this is the most efficient way of production. This type of workflow allows you to optimize your productivity and maximize your production output.
Click on the link below to watch a video on the difference between one-piece flow and batching the same part down an assembly line.
It is commonly believed by many teams that batching is a more efficient system, however, this is not always the case. As demonstrated in the video, implementing a one-piece flow system allows products to be produced at a consistent and steady pace. On the other hand, the batching process is slower and takes more time for the products to be finished.
5S
5S is a great lean tool to help you clean and organize your process by following the steps below. These easy steps were developed decades ago and have helped many companies start to improve the culture of their business by implementing 5S.
It is important to understand that companies often use the 5S methodology as a starting point for implementing lean improvements. Although management should initiate and support the 5S process, it is ultimately the responsibility of supervisors and workers to complete it. To make the process more effective, it is essential to empower the team to contribute suggestions and ideas. This approach can greatly improve employee morale and help build a culture of continuous improvement.
The 5S’s are;
Sort – Clean out rarely used items
Straighten – Organize and Label
Shine – Mop and dust the area
Standardize – Create rules that will keep the first 3S’s
Sustain – Audit areas to keep all the hard work you have put in place
Click on the links below to learn more about each 5S
Kanban
Kanban is a system that is used in production to trigger the ordering of more parts whenever they are needed. A Kanban signal can be an empty floor space where assemblies are stored before use or a card that is handed in when a parts bin is empty.
Kanban is a great way to help deliver parts to a process when needed. When Kanban’s are set up properly, it will lower inventory because the parts are delivered Just In Time (JIT) with no excess inventory required in the building.
Work Area Design
Work Area Design is a great way to evaluate each task completed in a work area. You will need to know every step and action taken in this work area to help improve the flow in this area. To review the Work Area Design your team will need the following;
Standard Operation Worksheets (SOW) – these worksheets will have the details of what is completed in each work area.
Layout of the Area – the layout is needed so you can use it as a tool to see how far someone moves from one work area to another.
With the SOW, walk through the process and identify each step to see how far the staff needs to travel to complete each task. After seeing the process, see what items should be moved to improve the flow of the work area. Every time you move an item closer to the point of use, you have improved the work area speed and efficiency.
Gemba
Gemba is a great lean tool for encouraging management and for staff to work together and problem-solve issues in a process. Gemba is the act of going to an area and observing what work is being done in that area. When the observer notices an issue, they will document what they see and talk to the worker in the area to get more details.
The observer then needs to work with the team to solve the issue. The issue must be resolved immediately to demonstrate its importance and your team’s commitment to prioritizing it.
The resolution to the issue can be broken into short and long-term fixes. The short-term fix should be in place before your team leaves the work area. The long-term fix should be agreed upon before you leave the area and the team agrees with the estimated completion date. Keep track of the date and communicate with the staff in the area if any changes will be made from the original agreement.
Educate your staff before you start Gemba so no one gets scared of the guy in the office watching them. It also helps if the person observing introduces themselves and tells the worker in the area why they are there. Make it a positive thing, let them know that you were there to help fix issues in the process and would like their help.
Kaizen
“Kaizen” is a Japanese word that means “improvement”. Working on Kaizen means working on the process of improvement. Every time you improve something, you are working on Kaizen. There are numerous ways to work on improvements, but one of my favorites is to conduct a Kaizen activity or event.
Kaizen Activity
During a Kaizen activity, you and your team will select a small improvement and work through the action items to solve the root cause of the issue. Typically, the issue is chosen from a continuous improvement tracker that your company maintains and tracks every time an improvement is identified in the process. Another place to find Kaizen activities is by improving on your biggest defect or quality issue.
Kaizen Event
A Kaizen event is done when you need to tackle a big issue and you might need a couple of days to correct the issue. The events are done with dedicated staff who are taken away from their daily tasks till the Kaizen event is over.
The event is broken down into the following steps, each step listed usually takes a day but it depends on how in-depth your project is.
- Train the team – show them how a Kaizen event works and what to expect.
- Go to the area and observe the issue – review the issue and look at any supporting documents that you may need.
- Brainstorm – talk through all the observations from the team and what solution will eliminate the root cause or improve the process.
- Implement the solution – install or make the changes to the process that you and your team agreed to.
- Review the solution – watch over the changes you made and make sure what you implemented in the process is working as intended.
Now that you know what Lean Manufacturing is and how you can use it to improve your business, what will you work on first?